Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office, Mr. Lucas Li, E-Mail: blockchain@elspub.com.
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team, Mr. Jay Zhuang, E-Mail: production@elspub.com.
About This Journal
Special Issues
Blockchain and AI for Secure and Trustworthy Cyber-Physical Systems
Special Issue Editor: Weizhi Meng, Xueqin Liang
Submission Deadline: 31 March 2026
Blockchain User Privacy and Anonymity: From Vulnerabilities to Protections
Special Issue Editor: Xinwen Fu, Shan Wang, Yue Zhang
Submission Deadline: 30 April 2026
AI and Blockchain Convergence—Toward Decentralized, Autonomous, and Trustworthy Digital Ecosystems
Special Issue Editor: Xiaotie Deng, Runhua Xu, Rui Qin, Xi Lin
Submission Deadline: 30 September 2026
Latest Articles
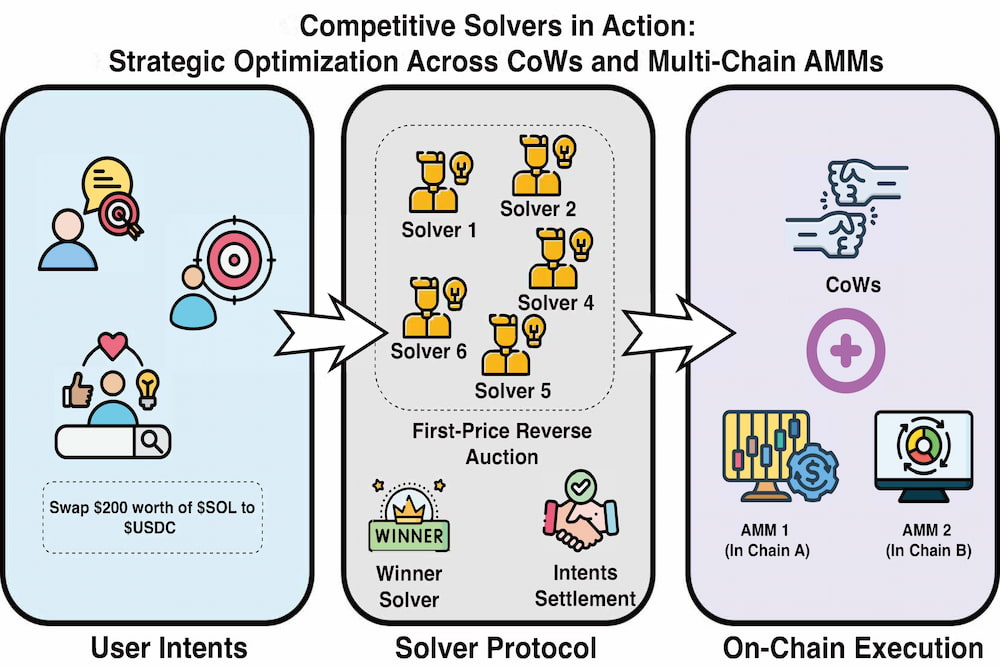
Competitive solvers in action: strategic optimization across CoWs and multi-chain AMMs
Published: 29 May, 2025
Editor's Choice
A critique on decentralized finance from a social, political, and economic perspective
Published: 31 Mar, 2023
Top Downloaded
A critique on decentralized finance from a social, political, and economic perspective
Published: 31 Mar, 2023