Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office.
Editorial Office
E-Mail: mechtech@elspub.com
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team.
Production team
E-Mail: production@elspub.com
About This Journal
Special Issues
Innovations in Electromechanical Systems through Intelligent Equipment and Digital Twin Technology under Industry 5.0
Special Issue Editor: Jiehan Zhou, Quanbo Lu, Zisheng Wang, Shouhua Zhang, Kai Ding
Submission Deadline: 30 April 2026
Latest Articles
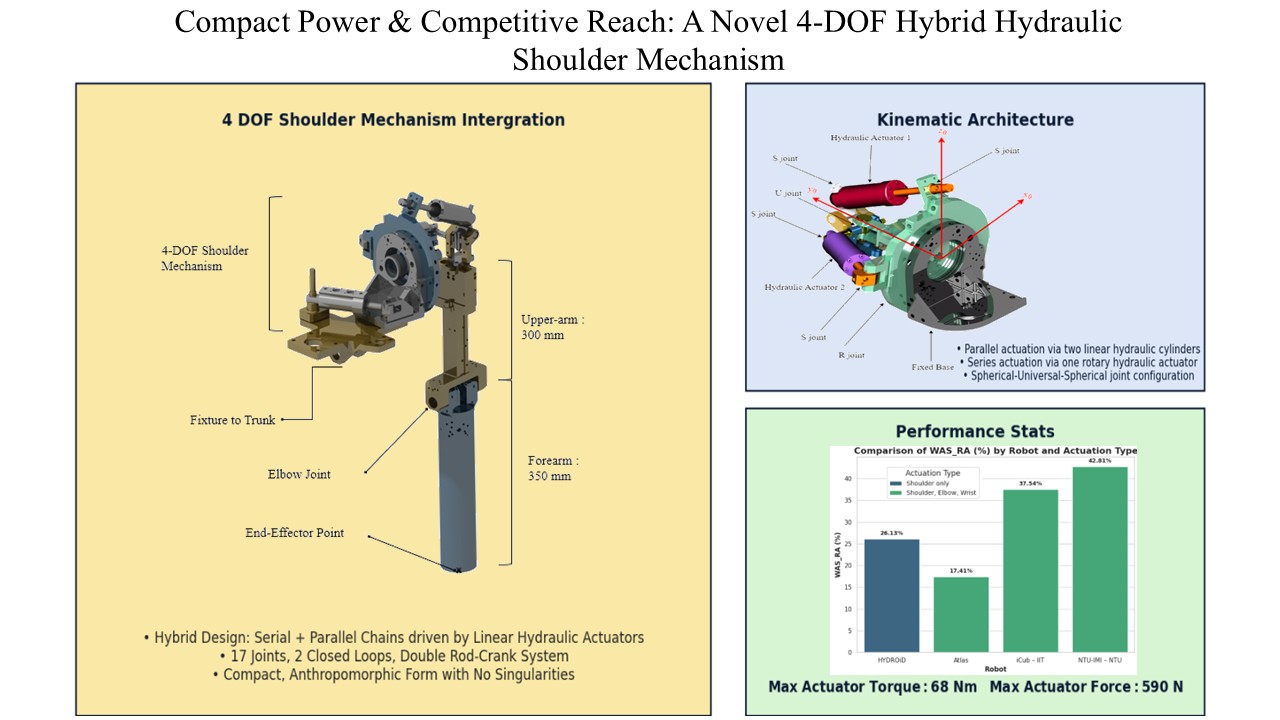
Design of a generic hybrid mechanism for hydraulic actuation in humanoid shoulder joints
DOI: 10.55092/mt20250005
Published: 28 Nov, 2025
Switching control of maglev yaw system based on average dwell time via backstepping approach
DOI: 10.55092/mt20250004
Published: 21 Aug, 2025
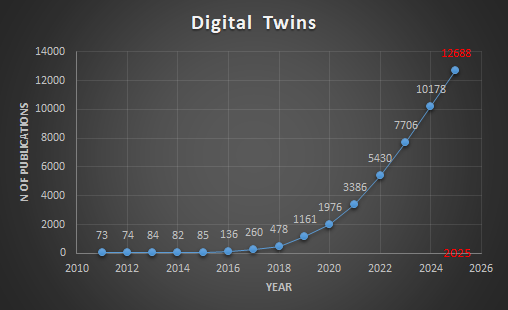
Digital Twins, history, metrics and future directions
DOI: 10.55092/mt20250003
Published: 16 Jun, 2025
Editor's Choice
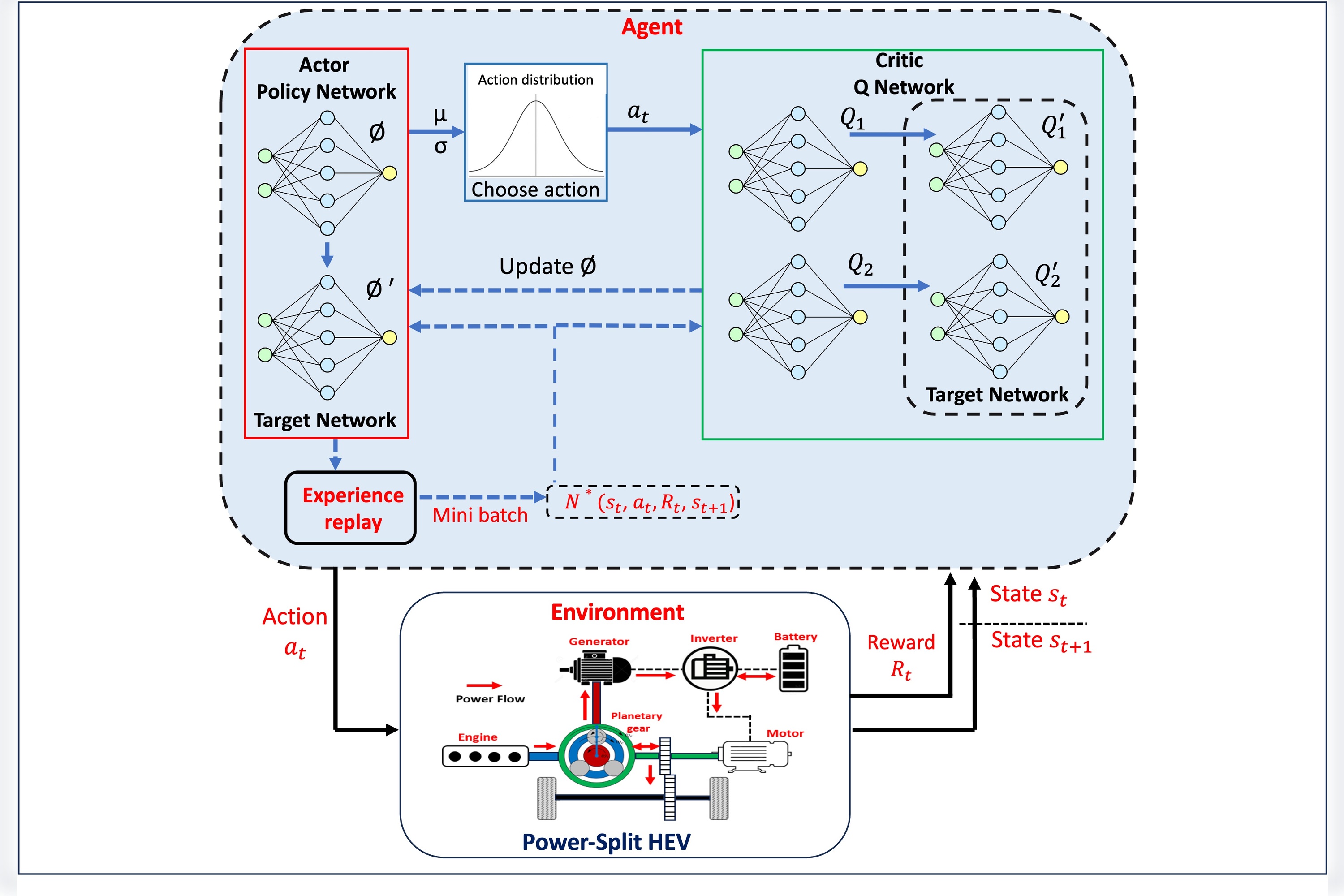
Adaptive learning-based energy management for HEVs using soft actor-critic DRL algorithm
DOI: 10.55092/mt20240005
Published: 31 Dec, 2024
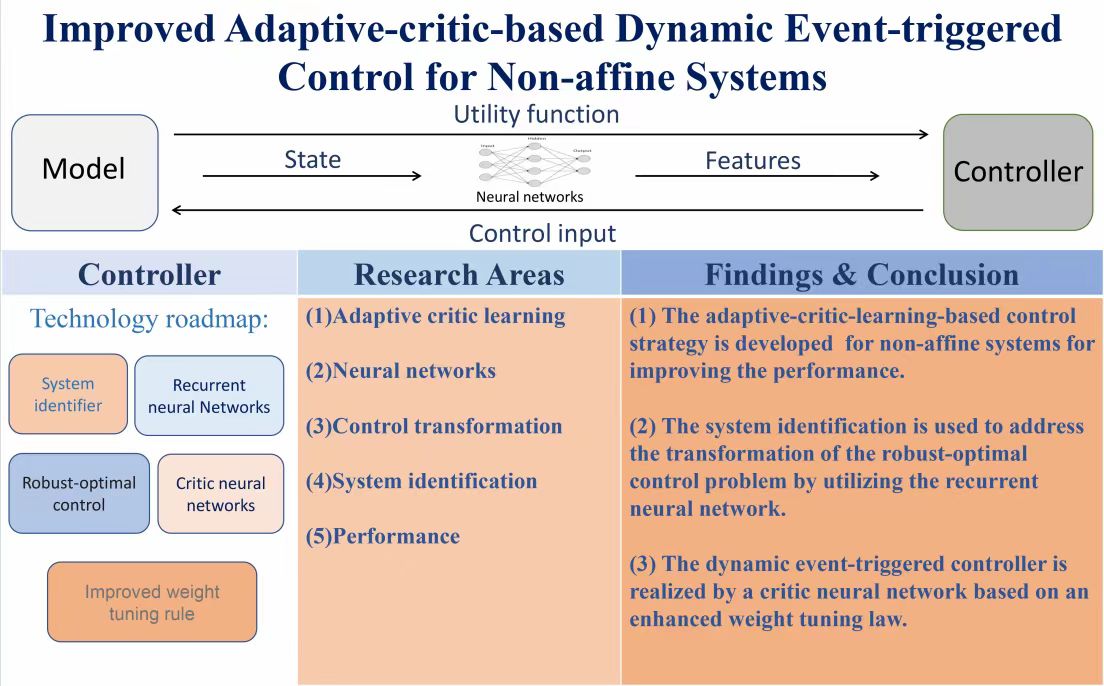
Improved adaptive-critic-based dynamic event-triggered control for non-affine systems
DOI: 10.55092/mt20230002
Published: 17 Aug, 2023
Top Downloaded
Recent advances in hand movement rehabilitation system and related strategies
DOI: 10.55092/mt20230003
Published: 11 Dec, 2023
Adaptive learning-based energy management for HEVs using soft actor-critic DRL algorithm
DOI: 10.55092/mt20240005
Published: 31 Dec, 2024
Digital Twins, history, metrics and future directions
DOI: 10.55092/mt20250003
Published: 16 Jun, 2025