Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office, Ms. Julia Luo, E-Mail: biofunmat@elspub.com.
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team, Mr. Jay Zhuang, E-Mail: production@elspub.com.
About This Journal
Special Issues
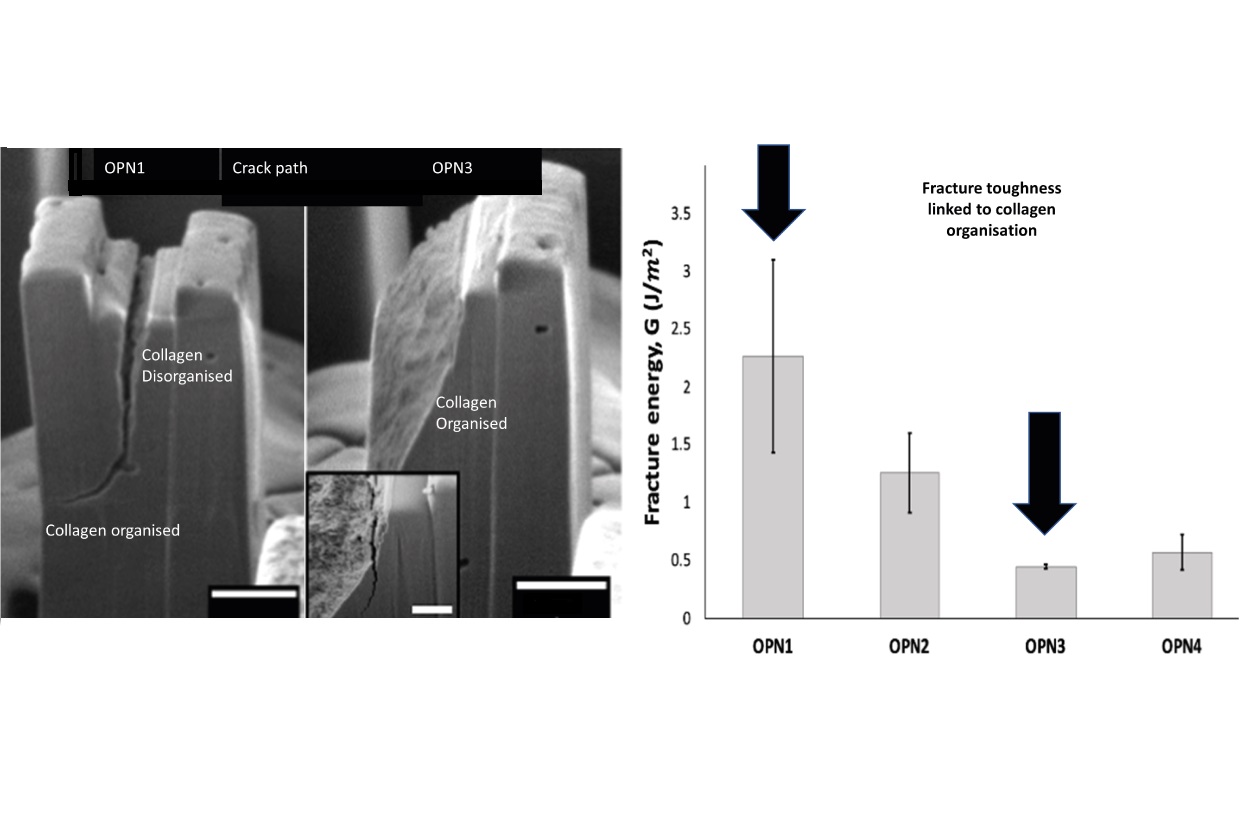
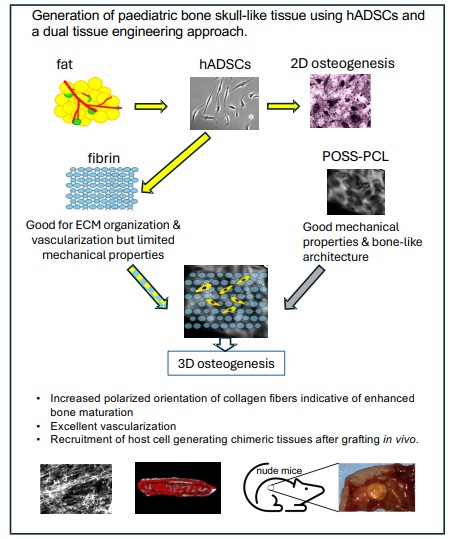
Biofunctional Materials for Tissue Regeneration
Special Issue Editor: Viola B. Morris, Chandra P. Sharma
Submission Deadline: 31 October 2026
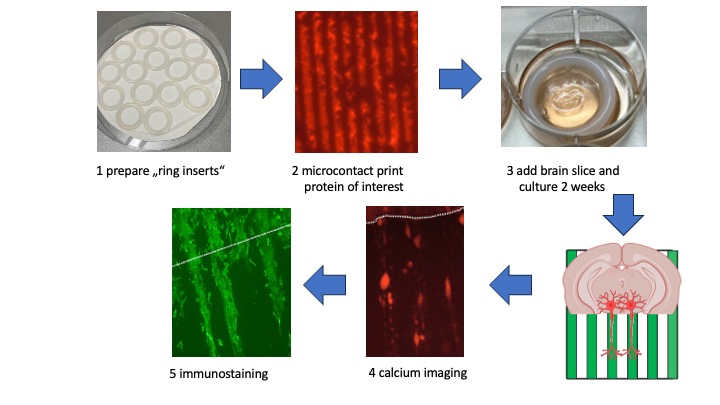
Biofunctional Materials for Clinical Diagnostics and Therapy
Special Issue Editor: Ming-Wei Chang, Zeeshan Ahmad
Submission Deadline: 31 July 2026
Latest Articles
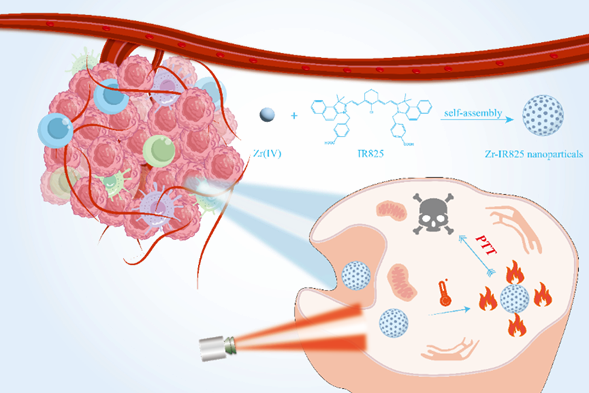
Design and synthesis of Zr-IR825 nanoparticles for photothermal therapy of tumor cells
DOI: 10.55092/bm20260001
Published: 12 Jan, 2026
Editor's Choice
Top Downloaded
Recent trends in natural polymer-based hydrogels for biomedical applications
DOI: 10.55092/bm20230009
Published: 21 Dec, 2023