Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office Ms. Ada Gu, E-Mail: rse@elspub.com
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team, Mr. Jay Zhuang, E-Mail: production@elspub.com.
About This Journal
Special Issues
Renewable Energy Transition and Sustainable Development
Special Issue Editor: Maurizio Filippo Acciarri, Silvana Stefani, Meruyert Narenova, Francisco Javier Ramos Real
Submission Deadline: 30 June 2026
Latest Articles
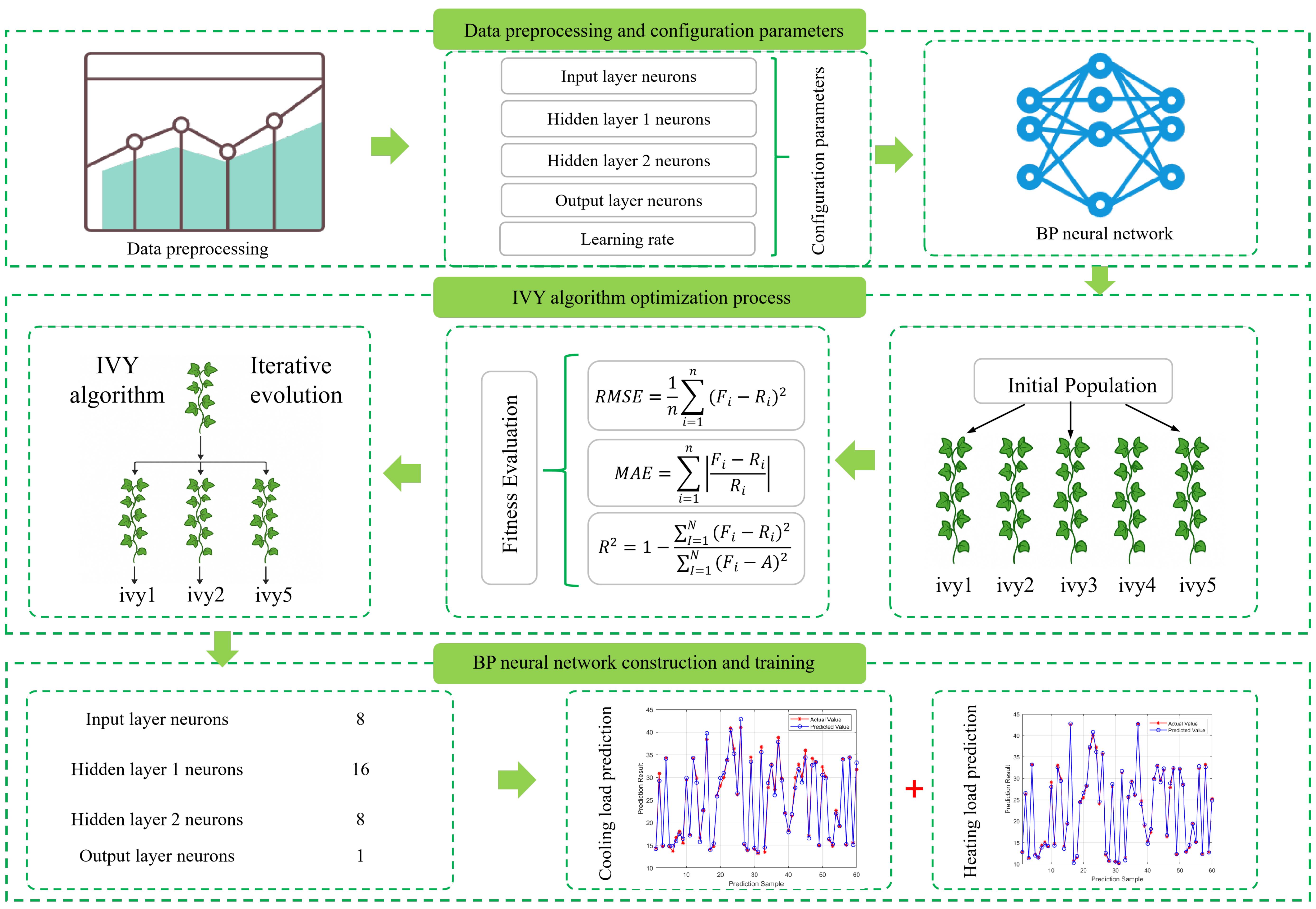
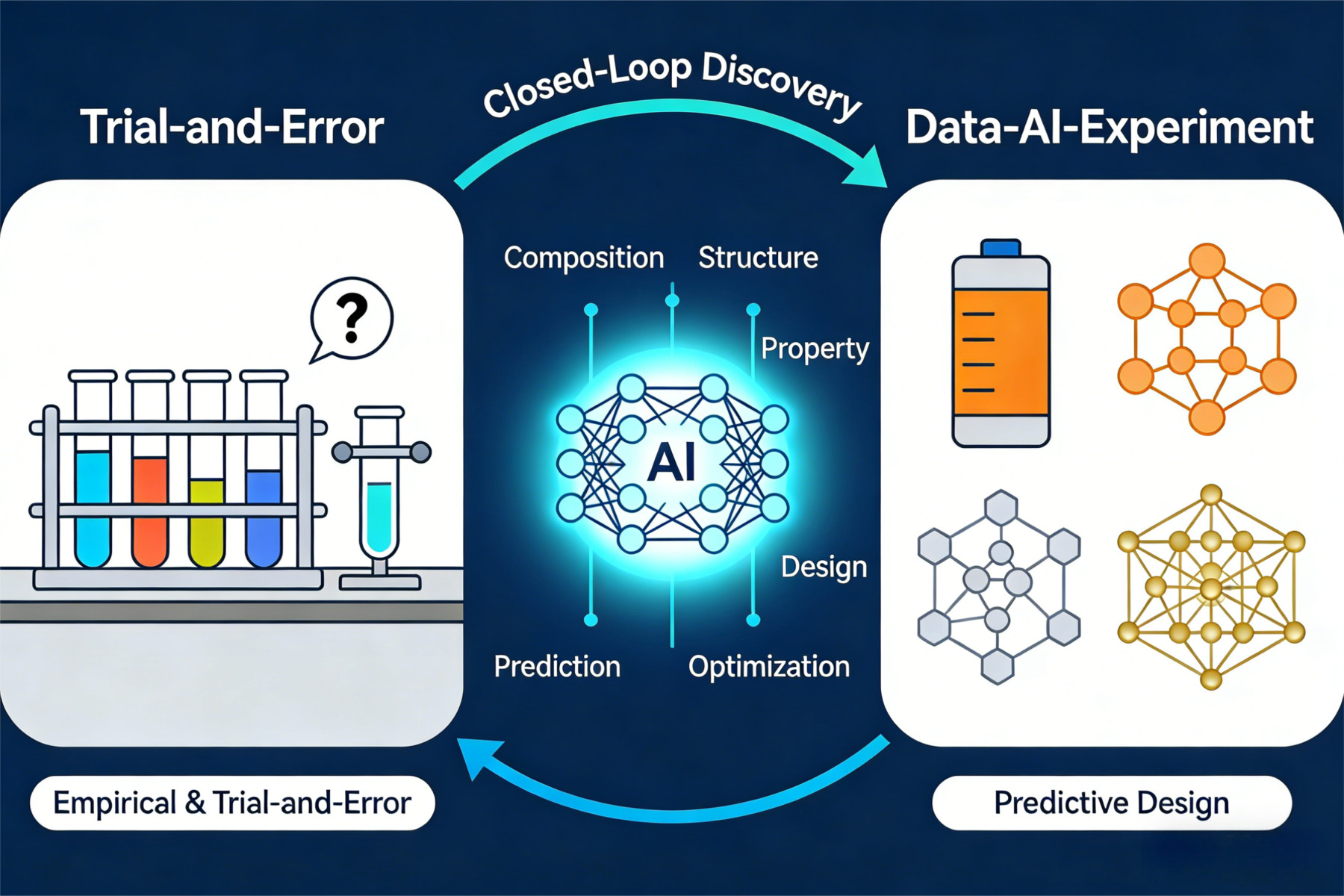
AI guided the development of materials science: a perspective
DOI: 10.55092/rse20260002
Published: 15 Jan, 2026
Editor's Choice
A Canadian case study of carbon dioxide removals and negative emission hydrogen production
DOI: 10.55092/rse20240005
Published: 04 Jun, 2024
Coal-derived porous carbon anodes for Na-ion batteries
DOI: 10.55092/rse20240004
Published: 26 Apr, 2024
Top Downloaded
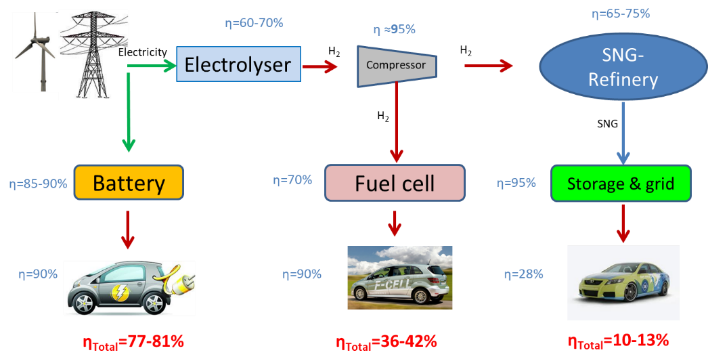
Heading towards low-carbon passenger car mobility: electricity vs hydrogen
DOI: 10.55092/rse20230002
Published: 10 Jan, 2023
Green Facade and Photovoltaic: a Multifunctional System
DOI: 10.55092/rse20230003
Published: 01 Mar, 2023
Coal-derived porous carbon anodes for Na-ion batteries
DOI: 10.55092/rse20240004
Published: 26 Apr, 2024