Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office.
Editorial Office
E-Mail: rl@elspub.com
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team.
Production Team
E-Mail: production@elspub.com
About This Journal
Special Issues
Learning Based Robot Path and Task Planning
Special Issue Editor: Guangliang Li, Shiqi Zhang, Dachuan Li
Submission Deadline: 31 July 2026
Human-in-the-Loop Robot Learning in the Era of Foundation Models: Challenges and Opportunities
Special Issue Editor: Jianzhuang Zhao, Xing Liu, Marta Lagomarsino, Francesco Tassi, Shufei Li, Chao Zeng, Jianshe Gao, Chenguang Yang
Submission Deadline: 30 June 2026
Human-Robot Interaction and Human-Centered Robotics
Special Issue Editor: Anqing Duan, Shuo Ding, Junling Fu, Elisa Iovene, Sipu Ruan, Peng Zhou, Chenguang Yang
Submission Deadline: 30 June 2026
Intelligent Vision-Driven Robotics
Special Issue Editor: Peng Zhou, David Navarro-Alarcon
Submission Deadline: 31 July 2026
Latest Articles
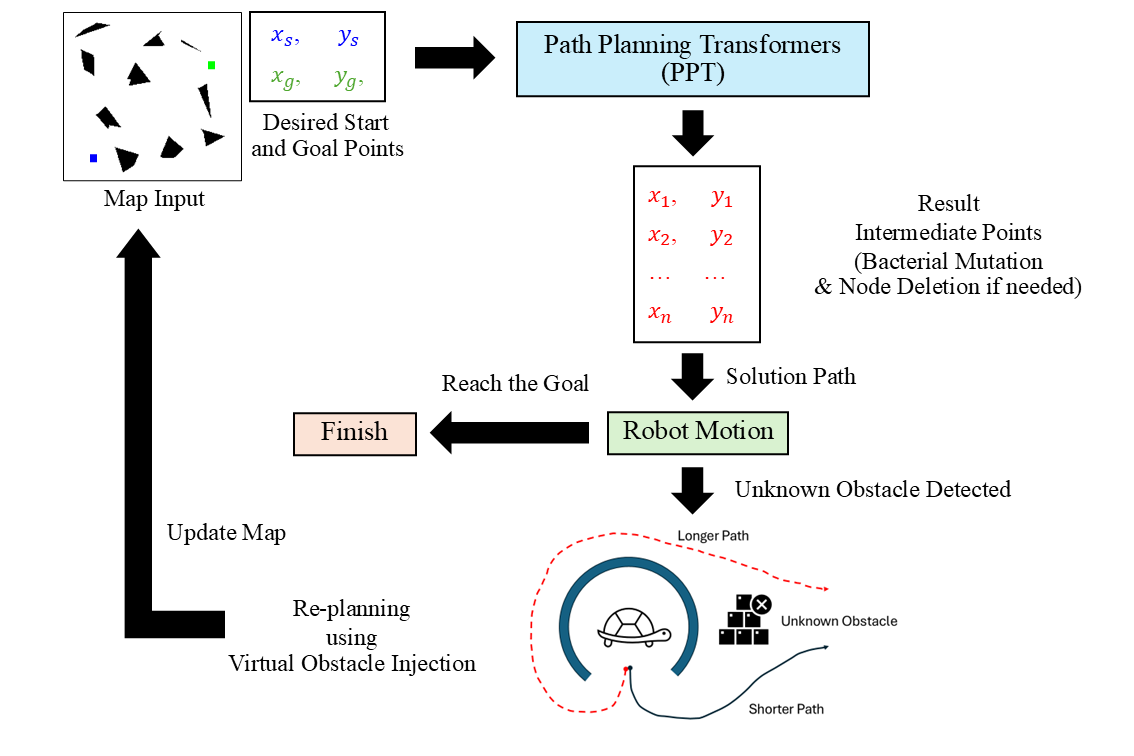
Path Planning Transformers supervised by IRRT*-RRMS for multi-mobile robots
DOI: 10.55092/rl20260005
Published: 05 Feb, 2026
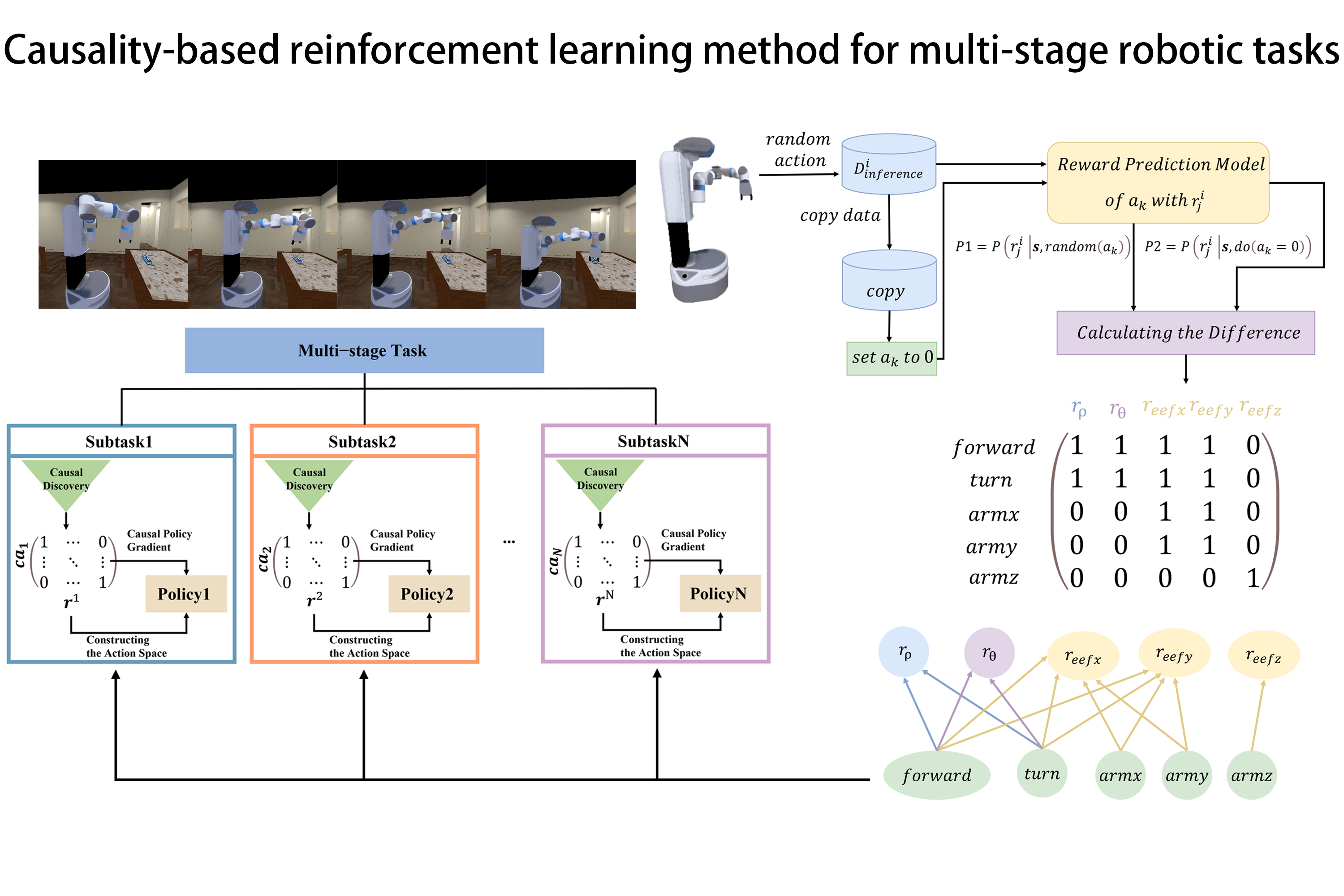
Causality-based reinforcement learning method for multi-stage robotic tasks
DOI: 10.55092/rl20260003
Published: 22 Jan, 2026
Editor's Choice
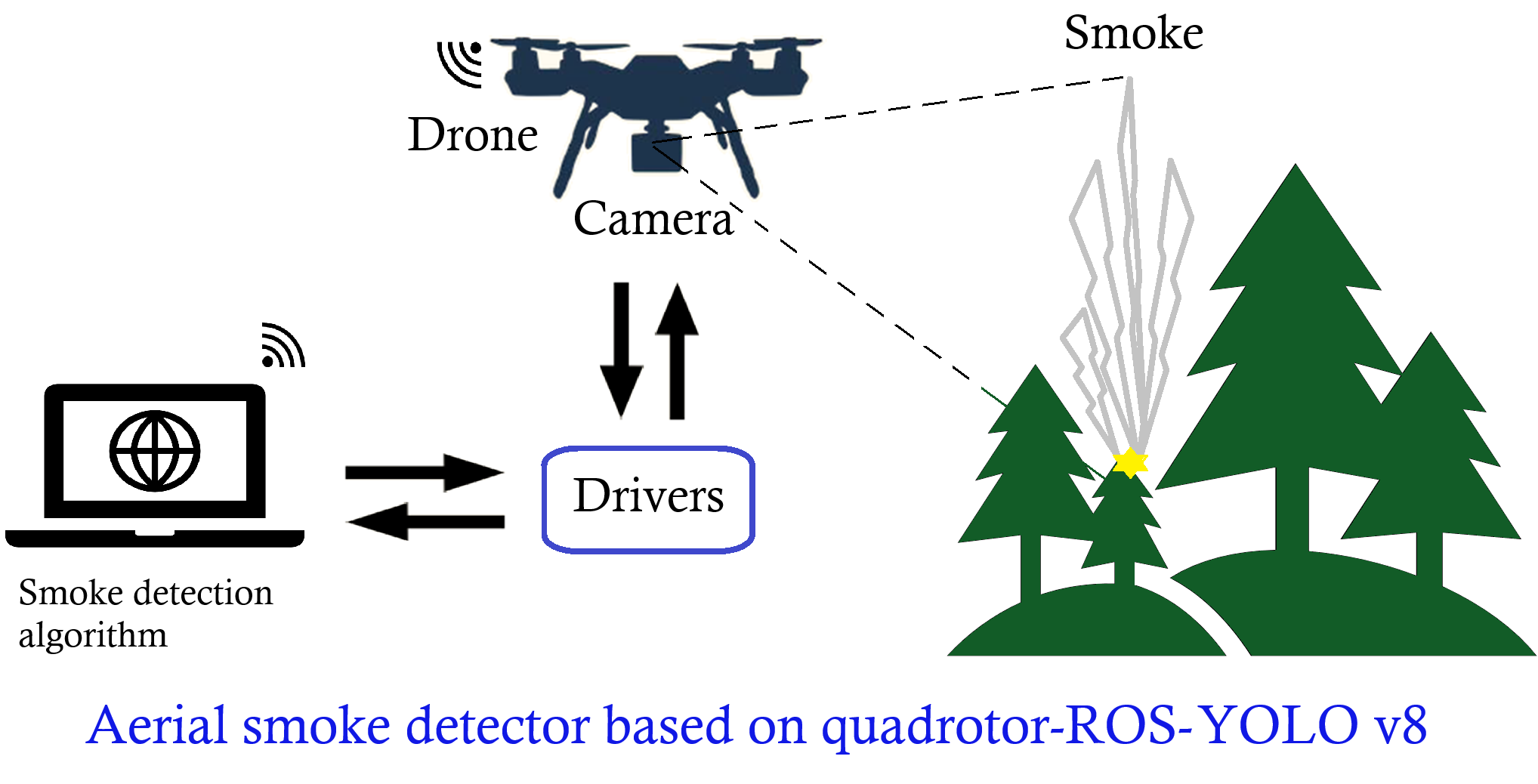
Quadrotor UAV-based smoke detector system using YOLOv8 towards wildfire prevention
DOI: 10.55092/rl20250001
Published: 20 Jan, 2025
Top Downloaded
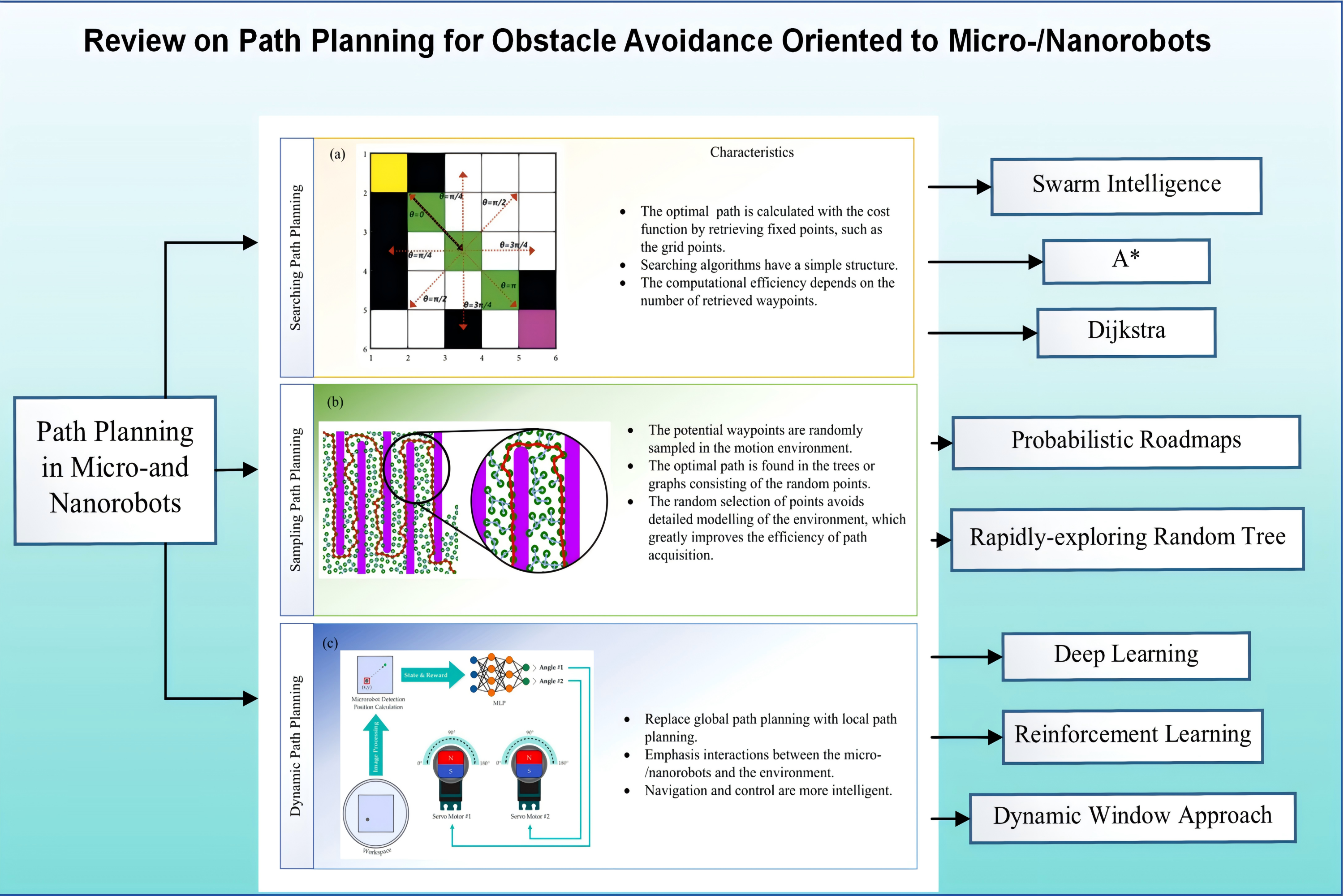
Review on path planning for obstacle avoidance oriented to micro-/nanorobots
DOI: 10.55092/rl20240002
Published: 14 Nov, 2024